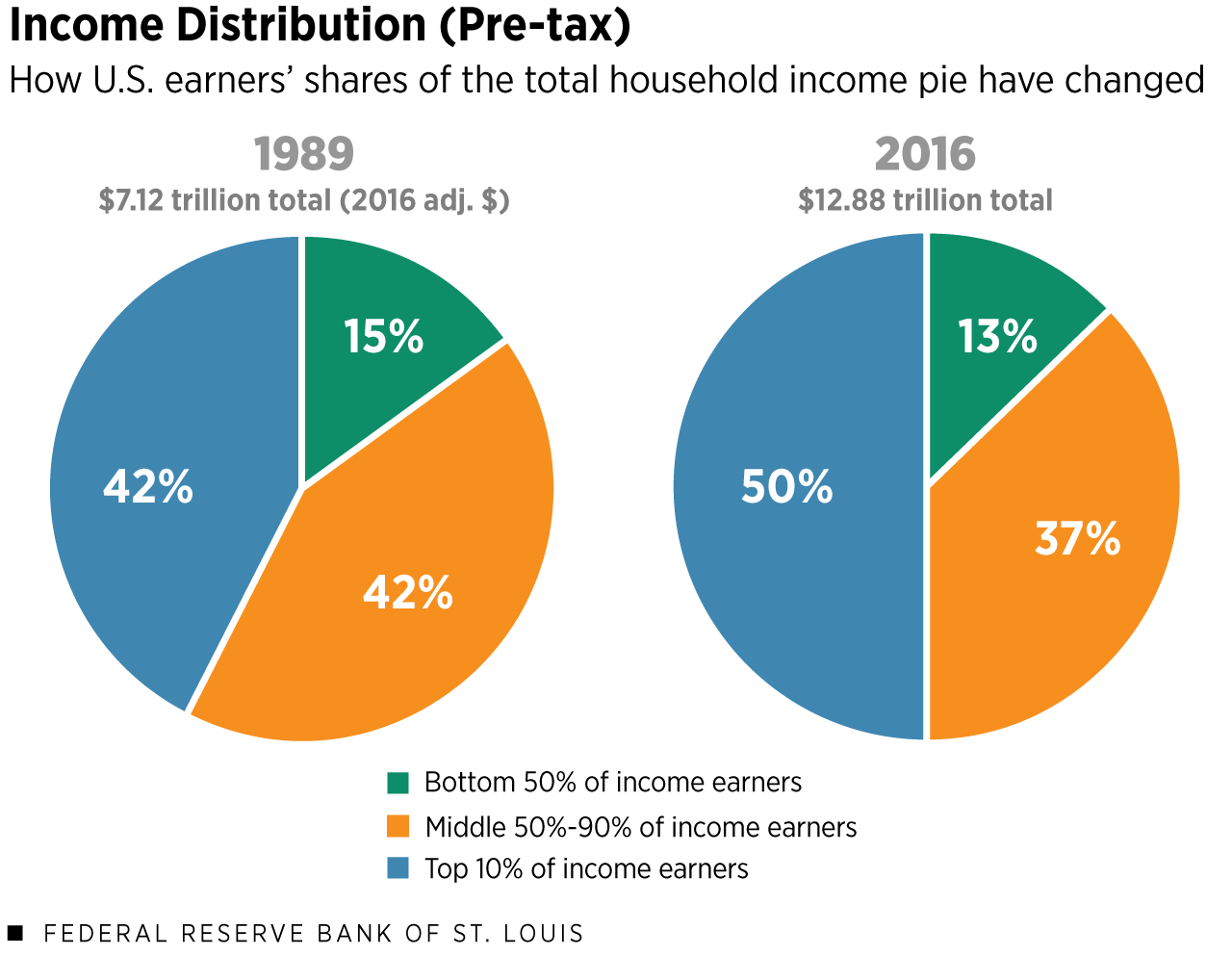
Income inequality remains one of the most pressing issues in contemporary society, raising questions about the fairness of a world where wealth is concentrated in the hands of a few. The stark divide between the rich and the poor has become more pronounced, exacerbated by the influence of billionaires and trillionaires who impact economic justice and societal well-being. While some argue that wealth redistribution through philanthropy can mitigate these disparities, others contend that the negative effects of extreme wealth cannot be overlooked. The ongoing debate around income inequality challenges us to rethink the structures and values that govern our economy. An exploration of this topic reveals complex layers of social, ethical, and economic implications that call for immediate attention and comprehensive solutions.
The disparity in wealth distribution, commonly referred to as economic inequality, highlights a significant imbalance in resources and opportunities across society. With extreme riches often held by a small percentage of the population, discussions around wealth redistribution and its effects on societal norms have intensified. This conversation includes examining the roles of affluent individuals, including billionaires and trillionaires, whose financial power can influence both philanthropy and public policy. The ethics of such wealth accumulation raises critical questions regarding the sustainability of our systems and the potential for achieving true economic justice. As we delve into this important dialogue, it becomes clear that addressing these issues is essential for fostering a fairer society.
Understanding Income Inequality in the Modern Economy
Income inequality refers to the unequal distribution of wealth and earnings among individuals in society. In many economies, particularly in developed nations, the gap between the wealthy and the poor has widened significantly over recent decades. This disparity is often reflected in the wealth amassed by billionaires, which stands in stark contrast to the income levels of average workers. The concentration of wealth in the hands of a few not only leads to economic instability but also raises ethical concerns about fairness in wealth distribution.
The implications of growing income inequality extend beyond financial metrics. It affects access to education, healthcare, and housing, creating systemic barriers for the lower classes. For a functional economy to thrive, measures such as wealth redistribution might be necessary, ensuring that everyone can benefit from the economic growth. Policies aimed at addressing income inequality could involve higher taxes on the ultra-wealthy and increased investment in public services, which in turn could lead to a more balanced and sustainable economic environment.
The Role of Philanthropy in Addressing Inequality
Philanthropy has emerged as a double-edged sword in the discussion of social justice and inequality. While wealthy individuals often donate large sums to charitable causes, critics argue that this can mask the systemic issues that create the need for such donations. For instance, billionaires like Bill Gates are hailed for their philanthropic endeavors in fighting poverty and improving global health. However, this form of wealth distribution can also perpetuate the existing power structures, potentially undermining the role of democratic institutions in addressing economic justice.
Furthermore, philanthropy can sometimes reflect the priorities of the wealthy rather than the needs of the communities they aim to help. When billionaires allocate funds based on personal interests or social trends, it can lead to skewed priorities that may not effectively tackle the root causes of poverty and inequality. As a society, we need to critically assess whether the impact of such philanthropic efforts leads to genuine progress or merely serves as a temporary relief for deeper, structural issues in income distribution.
Billionaires, Trillionaires, and Their Impact on Society
The rapid emergence of billionaires and the prospect of trillionaires have sparked intense debates about their role in society. As highlighted in recent discussions, while some argue that these ultra-wealthy individuals can drive innovation and economic growth, others point out that their immense wealth often comes at a significant cost to environmental sustainability and social equity. The challenge lies in balancing the benefits of their investments against the dangers of concentrated wealth which can lead to greater income inequality.
Moreover, the existence of trillionaires raises questions about the ethical implications of such wealth accumulation. In a world where a single individual could possess more wealth than entire nations, it prompts a necessary inquiry into the mechanisms that allow for such discrepancies. How can society ensure that the rise of billionaire wealth translates into benefits for all rather than exacerbating existing inequalities? Exploring alternative systems of wealth distribution and greater corporate responsibility could create a more equitable future.
Wealth Redistribution: A Path Towards Economic Justice
Wealth redistribution is often proposed as a viable solution to counteract income inequality and enhance economic justice. Proponents argue that redistributing wealth from the richest individuals can provide essential services and infrastructure to those who need it most, potentially closing the wealth gap. This approach can encompass various strategies, including progressive taxation, increased social spending, and investments in community initiatives aimed at improving the quality of life for the underprivileged.
However, the challenges inherent in wealth redistribution are complex and multifaceted. Critics often raise concerns about the effectiveness of government intervention, suggesting that poorly implemented policies can lead to inefficiencies and unintended consequences. Nevertheless, developing a robust framework for redistribution that promotes fairness while encouraging economic participation could foster a more inclusive society, ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
The Impact of Billionaires on Economic Justice
Billionaires wield substantial influence over economic policies and practices, provoking substantial discourse on their role in promoting or hindering economic justice. As individuals who have amassed immense wealth through various industries, their decisions and philanthropic efforts can significantly shape societal outcomes. For instance, while some billionaires invest in sustainable technologies, others might support policies that perpetuate systemic inequality, leading to questions about their collective responsibility toward fostering economic justice.
Moreover, the presence of extreme wealth can challenge democratic processes. When billionaires exert power over political contributions and lobbying, they may prioritize their interests over the needs of the general populace. Therefore, addressing the influence of wealth on political systems is crucial in the fight for economic justice. Ensuring transparent systems that hold these wealthy individuals accountable could foster a more equitable distribution of resources and opportunities.
Exploring Alternatives to the Current Capitalist Structure
The current capitalist structure has been critiqued for its propensity to generate extreme wealth for a select few while neglecting the broader population. In response, alternative economic systems have emerged that seek to create a more equitable framework. Concepts such as democratic socialism advocate for a balance between market freedoms and social safety nets, promoting both economic efficiency and social welfare. These systems prioritize the needs of the many over the wealth accumulation of the few.
Exploring these alternatives requires a multifaceted approach that emphasizes community empowerment, fair labor practices, and the democratic involvement of citizens in economic decision-making. By creating mechanisms that incorporate a wider range of voices in economic discussions, societies can craft solutions that work toward reducing both income inequality and the negative impacts of extreme wealth concentration.
The Role of Market Forces in Wealth Distribution
Market forces play a pivotal role in shaping the distribution of wealth within society. Many argue that a capitalist economy thrives on innovation and competition, leading to wealth generation. However, while markets can create opportunities, they can also exacerbate income inequality, particularly when concentrated in the hands of a limited number of individuals or corporations. The dynamics of supply and demand often overlook social equity, necessitating interventions to ensure that wealth serves a broader purpose beyond mere accumulation for the elite.
To achieve a balance between market efficiency and equitable wealth distribution, societies can implement regulatory frameworks that promote fairness. Encouraging corporate social responsibility, enforcing anti-trust laws, and prioritizing employee rights can help create an economic environment that uplifts all stakeholders rather than allowing wealth to flow upward disproportionately. By addressing market failures, governments can foster economic conditions that align more closely with the principles of justice and equality.
The Future of Billionaires and Wealth Concentration
Looking ahead, the growing concentration of wealth among billionaires raises pressing questions about the future of economic equity. The discussion around the potential emergence of trillionaires further complicates this landscape, as it highlights the magnitude of wealth accumulation in contemporary society. The implications of such wealth are profound, potentially leading to further income inequality unless countermeasures are put in place.
Societal responses to billionaire wealth will likely shape the economic landscape in the coming decades. If focused on inclusive growth and social investment, societies have the opportunity to harness the innovation and capital of the wealthy for collective benefit. Policies aimed at regulating wealth concentration and promoting equitable access to resources could pave the way for a more just economic framework, ensuring that growth benefits all members of society.
Philosophical Perspectives on Wealth and Inequality
Philosophy plays a crucial role in understanding the ethical dimensions of wealth and income inequality. The works of philosophers like John Rawls have inspired discussions on social justice, advocating that a fair society must safeguard the interests of its least advantaged members. By examining the moral implications of wealth distribution, philosophical inquiry challenges the status quo and prompts deeper reflection on what constitutes a just society.
Engaging with these philosophical frameworks can illuminate the ethical responsibilities that accompany immense wealth. It raises questions about the accountability of billionaires and their societal obligations. Philosophical perspectives can guide policymakers in crafting approaches to wealth distribution that align with principles of equity and justice, ensuring that economic systems serve the common good rather than catering solely to the affluent.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of income inequality in modern economies?
Income inequality arises from various factors including disparities in education, unequal access to resources, wage stagnation for low-paid workers, and the concentration of wealth among the super-rich. Wealth redistribution mechanisms, such as progressive taxation, aim to address these disparities by reallocating financial resources more equitably.
How does the impact of billionaires affect income inequality?
The impact of billionaires on income inequality is significant as their wealth accumulation often results in increased economic disparities. While billionaires can contribute to philanthropy and social initiatives, their financial power can lead to disproportionate influence over public policy, exacerbating income inequality if not balanced with effective wealth redistribution.
Can philanthropy effectively reduce income inequality?
Philanthropy can play a role in alleviating income inequality by funding social programs and initiatives aimed at helping the poor. However, critics argue that relying solely on philanthropic efforts, especially from billionaires, may not address the systemic issues causing inequality, such as inadequate wages and access to education. Comprehensive economic justice requires systematic reforms along with philanthropic contributions.
What role do trillionaires play in society and income inequality?
As potential trillionaires emerge, their role in society raises questions about economic justice and income inequality. Their immense wealth can fund innovations and job creation, potentially benefiting low-income populations. However, unchecked wealth concentration can undermine democratic institutions and limit opportunities for others, highlighting the need for policies that promote wealth redistribution.
How does economic justice relate to income inequality?
Economic justice seeks to create a more equitable distribution of wealth and opportunities. It challenges the structures that perpetuate income inequality, advocating for policies such as fair wages, decent working conditions, and progressive taxation. Addressing income inequality is a core component of achieving economic justice and ensuring that the benefits of economic growth are shared by all, not just the wealthy.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Extreme Wealth and Philanthropy | Discussion about whether billionaires are beneficial or harmful to society, highlighting their contributions to anti-poverty initiatives and green energy reforms. |
| Environmental Impact | Billionaires, particularly the top 1%, have a disproportionate carbon footprint, raising concerns about the sustainability of extreme wealth. |
| Diverse Perspectives | Panelists from various academic fields presented contrasting viewpoints on the implications of billionaires, bringing in elements of philosophy, ethics, and socioeconomic implications. |
| Redistribution of Wealth | Arguments for and against wealth redistribution, with perspectives on potential positive and negative outcomes for society. |
| Market Economy vs. Economic Systems | Debate on whether a market economy can help improve conditions for the poor, contrasted with calls for democratic socialism and other systems that prioritize equality. |
| Role of Luck in Wealth Creation | Acknowledge the arbitrary factors that contribute to wealth, which may not equate to meritocracy. |
| Conditions for Reducing Inequality | Suggestions included better labor rights, property-owning democracy, and facilitating immigration to reduce poverty. |
Summary
Income inequality is a pressing issue that continues to shape our society’s landscape. The debate surrounding extreme wealth and its ramifications has garnered attention, particularly in terms of environmental impacts and wealth redistribution. While billionaires offer philanthropic contributions, their disproportionate influence raises critical questions about their role and the structures that allow such wealth disparities. To effectively address income inequality, it is essential to explore multifaceted approaches that encompass both economic and ethical considerations.